Extensive Form Games
In the introduction to game theory and Nash Equilibrium, only normal form (matrix form) games were discussed. Now extensive form games will be discussed.
Extensive form games contain the following:
A game tree
A list of players
The names of players moving at each node
A set of allowable actions at each node
Payoffs specified at each node
Unlike normal form games, it is easy to depict sequential moves by players in extensive form games. For example, here is a game where Player 1 moves first, followed by Player 2:
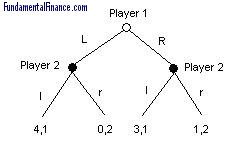
In this game, Player 1 can either choose L or R after which Player 2 can choose l or r. The list of strategies is slightly more complicated than in a normal form game. This is the proper way to list them:
- Player 1: {L,R}
- Player 2: {(l if L, l if R),(l if L, r if R),(r if L, l if R),(r if L, r if R)}
Player 2 actually has 4 strategies to choose from, not just 2. If we were to convert this game to normal form, it would look like this:
| | Player 2 |
|---|
| | l,l | l,r | r,l | r,r |
|---|
| Player 1 | L | 4,1 | 4,1 | 0,2 | 0,2 |
|---|
| R | 3,1 | 1,2 | 3,1 | 1,2 |
|---|
We can solve this game by backward induction. First, if Player 1 chooses L, then Player 2 will choose r. If Player 1 chooses R, then Player 2 will choose r. Player 1 is left with the option of choosing L and getting 0, or choosing R and getting 1. He'll choose R and the Nash Equilibria strategies will be (R,(l,r)) or (R,(r,r)).
Here's another quick extensive form game between an industry entrant and an industry incumbant. The Entrant can either stay out of the industry and not get any profits, or can enter the industry. If he enters, the incumbant will either fight him with a price war or accommodate and both firms will share the profits:
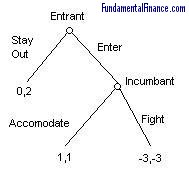
It looks scary: the Entrant might enter and lose money; however, he also knows that the Incumbant will lose money if he fights and still earn profits if he accommodates. The Incumbant has no credible threat. The Entrant will enter and the Incumbant will accommodate.
|
|